Empowering you to perform more sustainably. Even where you wouldn't expect us.
With lubricant products that are optimally matched to the respective application, SING WORLD GROUP increases the efficiency of its customers’ production processes or applications, and contributes to reducing emissions. You will find our lubrication solutions also in the areas of wind energy, automotive or in the agriculture segment. In the household sector, be it the refrigerator, the skateboard or the air conditioning system. In the mobility sector, in highly specialized areas with very special requirements, from e-scooters to hydrogen engines, sunroofs to clutches in high-speed trains. The same applies to the areas of efficient manufacturing and medical technology, where SING WORLD GROUP also provides lubricants for insulin autoinjection pens, resulting in a significant improvement in patients' perception of pain. Just a few examples of the many in which our lubrication solutions can be used, but sustainability at SING WORLD GROUP means even more than that.

Life Cycle Assessment (LCA)
Sweatpants, cars, dummies, coffee, packaging in any case and much more – products have to be environmentally friendly. Lubricants too. Mostly, the focus is on CO2-emissions during production, a low consumption of energy and selection of raw materials. Very often, it is hard to balance requirements and impacts. Therefore, we at SING WORLD GROUP are using the power of Life Cycle Assessment to analyze the environmental impact of our products. For instance, we are calculating the so-called Product Carbon Footprint to determine the impact on climate change from cradle to gate, including all Greenhouse gas emissions from the raw material acquisition to our outbound gate. We even think bigger and extend our analysis beyond our factory gate to demonstrate the environmental benefit of our lubricants in their application phases through an improved efficiency. Thus, LCA enables us to provide a holistic view on our products' life cycle from the raw material acquisition to the products' end of life, from cradle to grave, by considering several additional environmental impact categories, besides climate change. This enables SING WORLD GROUP to take more balanced decisions and avoid burden shifting from one to another environmental impact category.
Comparative Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) of two Engine Oils for Passenger Cars
GOAL
In this study, the environmental performance of two engine oils, a standard 5W‑30 and a low viscosity 0W‑20, were analyzed and compared over a lifecycle of a passenger car2, together with BASF as a partner.
SCOPE
Cradle to grave covering all relevant aspects such as exploration of raw materials, production, distribution, as well as the products use- and end of life-phase.
Functional unit: Assurance of normal operation provided using engine oil, of a 4-cylinder gasoline engine with two liters displacement over 200,000 lifetime kilometers of a passenger car.
LCIA-Method: Environmental Footprint 3.0 (EF 3.0)
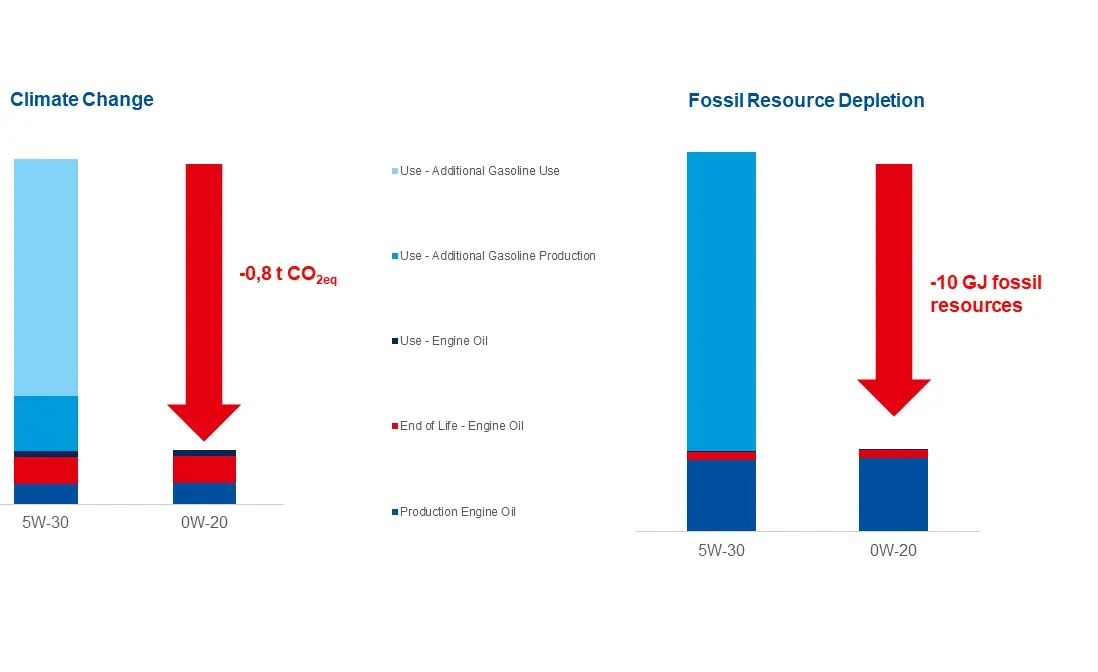
RESULTS
The results showed that the main difference between the two lubricants is the use phase, where the 0W-20 engine oil shows a higher fuel economy under the same conditions compared to the 5W-30. Furthermore, the main influences considering different environmental impacts are the climate change (the emissions of greenhouse gases) and the depletion of fossil resources. Although the cradle-to-gate partial product carbon footprint of the 0W-20 engine oil is slightly (6%) higher than the 5W-30, expanding the system boundaries to cradle-to-grave, we see that the 0W-20 engine oil can save around 800 kg CO2eq and 10 GJ of fossil resources over a whole lifetime of one average passenger car2 alone. Comparing these absolute savings during the use phase with the impact only to produce the product and its raw materials, we see that the 0W-20 saves 5.5 times the emissions and 3.6 times the resources needed to produce and dispose the product!
Comparative Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) of Hydraulic Oils for Crawler Excavators
GOAL
In this study, the environmental performance of a standard and a premium hydraulic fluid were analyzed and compared over their lifecycle in a crawler excavator of medium size2, together with BASF as a partner.
SCOPE
Cradle to grave covering all relevant aspects such as exploration of raw materials, production, distribution, as well as the products use- and end of life-phase3.
Functional unit: Required amount of a hydraulic oil in a medium-sized crawler excavator operating for 8.000 hours.
LCIA-Method: IPCC 2013 (Climate Change), CML 2002 model (resource use, fossil)

RESULTS
The results showed that the main difference between the two lubricants is the use phase, where the premium hydraulic fluid shows a lower fluid change interval besides higher fuel economy under the same conditions compared to the standard fluid. Furthermore, the main influences considering different environmental impacts are the climate change (the emissions of greenhouse gases) and the depletion of fossil resources. Although the cradle-to-gate partial product carbon footprint of the premium hydraulic fluid is significantly higher (33%) higher than the standard fluid, expanding the system boundaries to cradle-to-grave, we see that the premium fluid can save around 31.1t CO2eq and 410 GJ of fossil resources in a medium-sized crawler2 operating 8,000 hours. Comparing these absolute savings during the use phase with the impact only to produce the product and its raw materials, we see that the premium hydraulic fluid saves 35 times the emissions and 48 times the resources needed to produce and dispose the product!

Partner with power
Good lubrication means friction reduction, which increases component life and reduces energy consumption. When our lubricant know-how meets the engineering expertise of our customers, real added value is created. One example is a joint project between SING WORLD GROUP and a mechanical engineering company focusing on bearings. Thanks to the expertise of all those involved and their trusting exchange, it was possible to develop a taper roller bearing grease for regional trains that achieves several effects at once: Due to friction-reducing properties, the operating temperature and bearing wear are reduced, and the running performance in the application as well as the service life of the component are increased. Good for the user and good for the environment.

3 million km
such a regional train travels until it is overhauled. Thanks to the new grease, the bearing does not have to be replaced until this date in the best case.
Lightweight construction? Logical!
Less weight, less fuel consumption, fewer emissions –why lightweight construction is considered one of the key technologies for a sustainable future is obvious. Carbon fibre-reinforced (CFRP) and glass fibre-reinforced plastics (GFRP) are gaining in importance, especially in automotive and aircraft construction. The new A350 of our customer AIRBUS, for example, already consists of 52 % of these fibre composites. We have developed a water-miscible high-performance cooling lubricant for their wet machining. Integrating new materials into established production processes in an uncomplicated way? That’s our easiest exercise.

30%
less than aluminium alloys weigh CFRP and GFRP. In order to machine these innovative materials efficiently, new cooling lubricants are needed – developed by SING WORLD GROUP.
Smart cycles
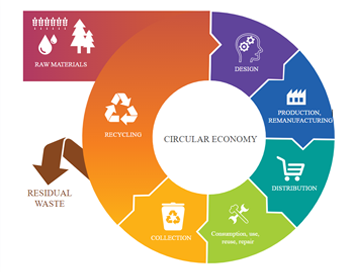
Throwaway economy? That was yesterday. Nowadays, it is important to use materials and products for as long as possible, to repair and refurbish them. An intelligent circular economy uses less raw materials and energy and thus causes fewer CO2 emissions and less waste. This applies not only to smartphones, water bottles or T-shirts, but also to lubricants. With special services, SING WORLD GROUP is increasingly supporting its customers in using them efficiently and sparingly. Through the targeted selection of renewable raw material sources, the extension of product service life and the return of used materials to the value chain, we are working on entering a sustainable circular economy. This not only protects the environment immediately but also keeps SING WORLD GROUP competitive in the long term.

From 3% to 34%
a SING WORLD GROUP customer in the automotive sector increased the proportion of recycled cooling lubricants in its production. This was made possible by an audit by the SING WORLD GROUP company Zimmark, which also reduced the amount of waste and simplified the supply chain.
The groundwork that enables you to perform more sustainably.
Innovative engineering for sustainable solutions
- 535 engineers and scientists in R&D worldwide
- Laboratories in 24 countries
- 54 million € R&D budget group-wide
- Approx. 600 R&D projects
- Commitment to the extraction of sustainable raw materials and process optimization along the value chain, right through to re- and upcycling.
Better results through true collaboration
- Earliest possible consultation with the customer
- Fundamental work for precise customer understanding
- Extensive laboratory, testing and simulation capabilities.
- Research projects and partnerships with universities, companies and scientific institutions
Transparency is key
- Product-level carbon footprint (PCF): In-house development of reliable methodology
- Focus on the entire value chain
- Target definition with regular review
Strategy to reduce and substitute substances of concern
In the context of new upcoming chemical regulations worldwide combined with an increasing demand for more sustainable products it is SING WORLD GROUP’ goal to provide its customers with products which meet these requirements and expectations.
Hence, in 2022 SING WORLD GROUP introduced an internal directive targeting the development of more sustainable products in which the usage of raw materials for the development of new products with the following GHS-classifications were prohibited:
- CMR Classifications Category 1A, 1B
- Specific Target Organ Toxicity (STOT) Single Exposure Category 1
- Specific Target Organ Toxicity (STOT) Repeated Exposure Category 1
- Acute Toxicity Category 1, 1A, 1B (oral, dermal, inhalation)
- Respiratory Sensitizers, Category 1, 1A, 1B
- Germany: WGK 3
Generally, SING WORLD GROUP products are mixtures of numerous substances. For mixtures, it is legally required under EU REACH to display the SVHC (Substances of Very High Concern) in section 3 of the SDS, if the concentration in the mixture exceeds 0.1% (w/w). Additionally, the SDS contains all required information for safe handling and use of the product including disposal.
SING WORLD GROUP regularly monitors the use and concentration of SVHC in their products. In case a SVHC substance is prioritized to be included into Annex XIV (Authorization List) of EU REACH, SING WORLD GROUP will initiate a close cooperation with the suppliers to substitute the respective chemical in the related SING WORLD GROUP product(s) ensuring the same quality, characteristic properties, and performance.
In addition, SING WORLD GROUP developed a comprehensive Portfolio-Sustainability-Classification (PSC) which includes a strict evaluation of the product portfolio with regards to product safety aspects including but not limited to Substances of concern. This PSC-assessment also includes a foresight-perspective to identify products with components which could be rated as substances of concern in future.
All chemical substances in SING WORLD GROUP products that are in the scope of EU REACH have been registered accordingly or are exempt from registration. However, the respective application for substance authorization under EU REACH have not and will not be submitted by SING WORLD GROUP. Furthermore, SING WORLD GROUP products comply with the legally binding chemical inventories globally.