Hydrocracked Base Oils that typically have low volatility and high viscosity indexes.
Group III & III+ Base Oils Overview
Group III and III+ base oils are highly refined oils classified as "synthetic" in many regions, particularly in the United States. They are derived from crude oil but undergo extensive processing, such as hydrocracking, hydroisomerization, and severe hydrofinishing. These processes enhance their molecular structure, giving them properties comparable to synthetic oils.
Key Characteristics
-
Group III:
- Saturates Content: Greater than 90%.
- Sulfur Content: Less than 0.03%.
- Viscosity Index (VI): Higher than 120.
- Purity: Extremely low levels of impurities due to severe hydrocracking and hydroisomerization.
-
Group III+:
- A subcategory of Group III oils with even higher performance.
- Viscosity Index (VI): Typically exceeds 130.
- Improved low-temperature properties and thermal stability compared to standard Group III oils.
Production Process
- Severe Hydrocracking: Breaks down crude oil into smaller, more uniform molecules.
- Hydroisomerization: Rearranges the molecular structure to improve performance characteristics like oxidation stability and cold-weather fluidity.
- Hydrofinishing: Further removes impurities and enhances color and oxidation resistance.
Advantages
- Synthetic-Like Performance:
- High thermal and oxidative stability.
- Excellent low-temperature properties for cold-start performance.
- Cost-Effectiveness:
- Less expensive than true synthetic oils (Group IV).
- Wide Availability:
- Dominates the market for modern automotive and industrial lubricants.
Disadvantages
- Limited Extreme Performance:
- While superior to Groups I and II, they may not match the high-temperature performance of PAOs (Group IV).
- Synthetic Label Controversy:
- In some regions, they are not considered "true synthetics" despite similar performance.
Applications
- Automotive Lubricants:
- Engine oils designed for modern engines, including high-performance and turbocharged engines.
- Industrial Lubricants:
- Hydraulic fluids, gear oils, and turbine oils.
- High-Performance Applications:
- Products requiring excellent oxidative and thermal stability under severe conditions.
Comparison with Other Groups
- Group II: Group III has a higher viscosity index and is more thermally stable.
- Group IV: PAOs outperform Group III in extreme conditions but are more costly.
- Group III+: Offers better performance than standard Group III, often bridging the gap with Group IV.
For further information and detailed specifications, please contact us.
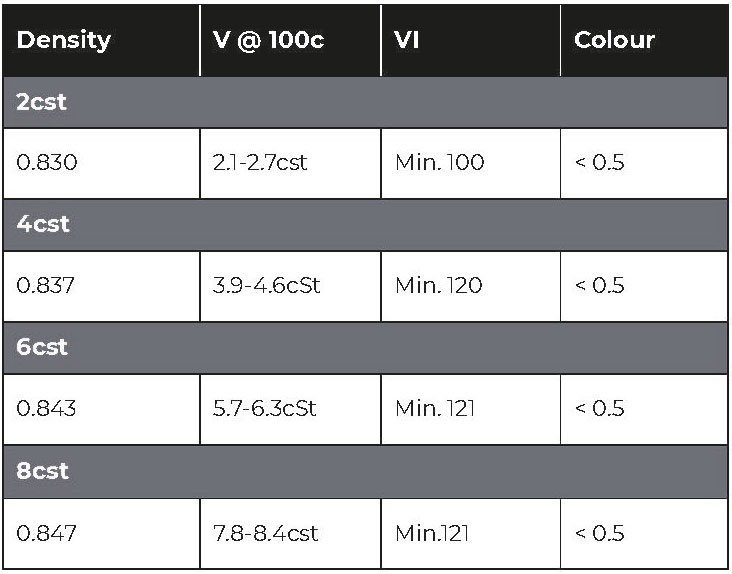
Please note: Colour of base oil will vary according to source and refinery process.