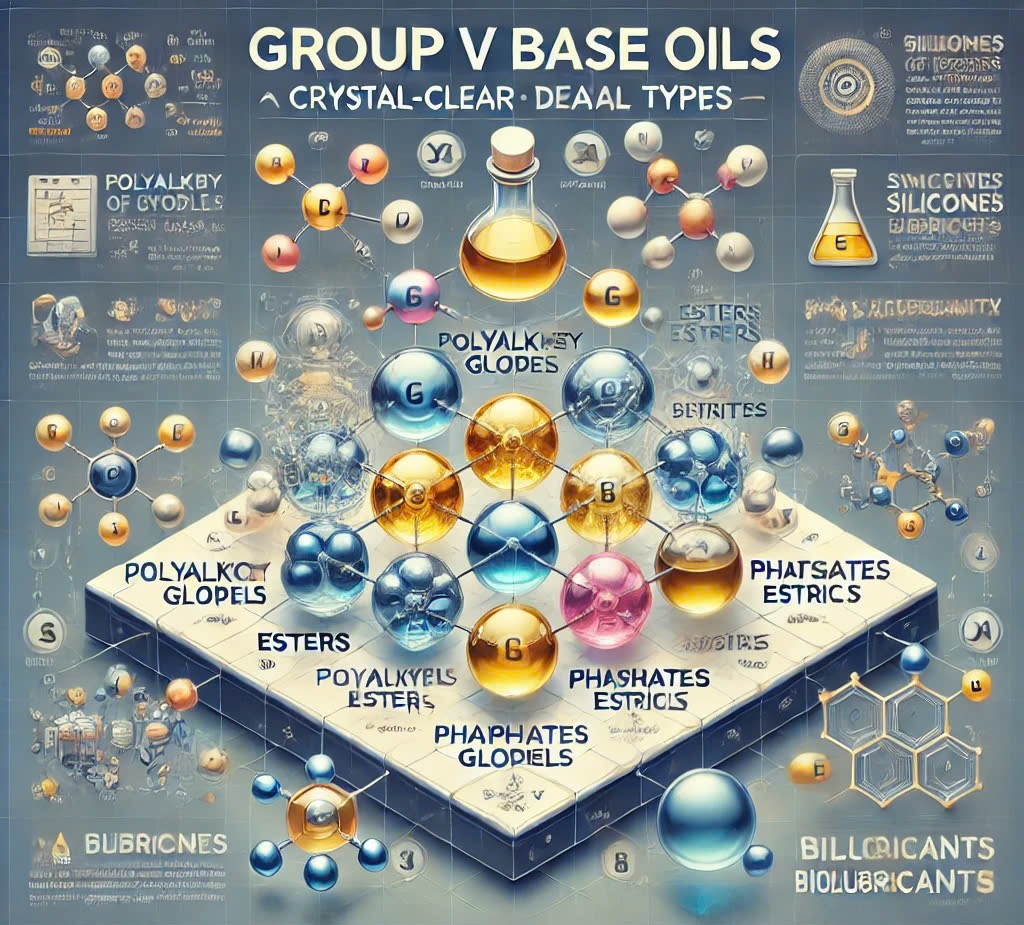
Group V base oils encompass all base oils that do not fall under Groups I-IV. This category includes a variety of specialized oils such as silicone, phosphate ester, polyalkylene glycol (PAG), polyolester, and biolubricants. These oils are often blended with other base stocks to enhance specific performance characteristics. For instance, PAO-based compressor oil is sometimes combined with polyol ester to achieve improved properties.
Esters, a common type of Group V base oil, are widely used in lubricant formulations to boost the performance of existing base oils. Known for their ability to withstand higher temperatures, esters offer exceptional detergency compared to PAO synthetic base oils. This advantage translates to extended operating hours and enhanced durability.
When selecting a base oil, it’s crucial to ensure it is suited to your specific application, as well as the temperature range and operating conditions of your facility.
COMPARISON WITH GROUP IV (PAOS)
Group IV oils are fully synthetic hydrocarbons offering a high viscosity index and oxidative stability.
Group V oils, while also synthetic or semi-synthetic, include a broader variety of chemistries, such as esters and silicone, providing more specialized functionalities.